Exploring the Reactions Using Palladium Carbon Catalysts
Introduction
Catalysis is a key process in various industries, enabling the transformation of reactants into valuable products with increased efficiency. Among the catalysts widely used in catalytic reactions, palladium on carbon (Pd/C) stands out for its exceptional catalytic efficiency and versatility. This powerful combination of palladium nanoparticles supported on a carbon substrate offers unique properties that make Pd/C catalysts highly valuable in a range of applications. In this article, we will explore the diverse reactions that Pd/C catalysts transform and how they enhance catalytic efficiency.

Figure 1. Palladium Carbon Catalysts
Reactions Using Palladium on Carbon
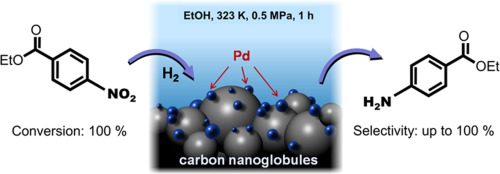
1. Hydrogenation Reactions
Pd/C catalysts are extensively employed in hydrogenation reactions, where hydrogen gas is added to unsaturated compounds to form saturated derivatives. The catalytic activity of Pd/C enables rapid hydrogenation, reducing the reaction time and increasing the yield of the desired product. This makes Pd/C catalysts highly valuable in pharmaceutical, fine chemical, and petrochemical industries for the synthesis of various compounds, such as pharmaceutical intermediates, flavors, and fragrances.
2. Cross-Coupling Reactions
Cross-coupling reactions involve the formation of carbon-carbon bonds between two or more reactants. Pd/C catalysts, especially those based on palladium nanoparticles, are widely utilized in cross-coupling reactions, such as Suzuki-Miyaura and Heck reactions. These catalysts facilitate the coupling of diverse substrates, including aryl, vinyl, and heteroaryl compounds, enabling the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
3. Carbonylation Reactions
Carbonylation reaction is another common reaction using palladium on carbon catalysts. It involves the introduction of a carbonyl group into organic compounds, expanding their functionality and potential applications. Palladium on carbon catalysts in carbonylation reactions enables the synthesis of a variety of compounds, including esters, amides, and carboxylic acids. These reactions play a crucial role in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and polymer industries, and Pd/C catalysts provide high catalytic activity and selectivity in driving carbonylation transformations.
4. Nitrogenation Reactions
Nitrogenation reactions refer to the introduction of nitrogen-containing functional groups into organic molecules, enabling the synthesis of amines, amides, and other nitrogen-containing compounds. Palladium on carbon catalysts have proven to be efficient catalysts in nitrogenation reactions such as reductive amination, Buchwald-Hartwig amination, and amide formation. These reactions are of great importance in pharmaceutical synthesis, where amines and amides serve as essential building blocks.
5. Carbon-Heteroatom Bond Formation
Pd/C catalysts are also valuable in carbon-heteroatom bond formation reactions, such as the Buchwald-Hartwig amination and the Mizoroki-Heck reaction. Through these transformations, carbon-nitrogen, carbon-oxygen, and carbon-sulfur bonds are formed. Pd/C catalysts efficiently promote these reactions, allowing the synthesis of a wide range of functionalized organic molecules with diverse applications in pharmaceutical and material sciences.
6. Reduction Reactions
Pd/C catalysts are effective in various reduction reactions, including the reduction of functional groups, such as carbonyls, nitro groups, and olefins. The catalytic activity of Pd/C facilitates these reductions, providing milder reaction conditions and reducing the need for harsh reagents. So, the process is more environmentally friendly, and we could maintain high yields and selectivity at the same time.
7. Other Reactions
In addition to the mentioned applications, Pd/C catalysts find utility in several other reactions, including decarbonylation, dehalogenation, and cyclization reactions. Their versatility and efficiency make them valuable tools in synthetic chemistry, facilitating the development of new materials and pharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
In a word, palladium on carbon catalysts (Pd/C) are powerful tools for enhancing catalytic efficiency in a range of applications. From hydrogenation and cross-coupling reactions to carbon-carbon bond formation and reduction reactions, Pd/C catalysts play a pivotal role in synthetic chemistry. Their exceptional activity, selectivity, and stability make them indispensable in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and material sciences. The continued exploration and optimization of Pd/C catalysts will undoubtedly lead to further advancements and innovations in catalysis, driving progress in chemical synthesis.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a leading supplier of high-quality precious metal catalysts, including palladium on carbon. All of them are well-packed and offered at reasonable prices. Welcome to check our site for more information.